Research progress of key LED technologies in the first half of 2024
Although the industry is becoming more and more inward-looking, the LED display industry has not stopped looking for new ways to be different, and technical and functional breakthroughs are often the first step. The birth of each of the following new technologies is the result of countless days and nights of careful research by people in the LED display industry. Of course, this is just the tip of the iceberg. In 2024, when new technologies are constantly being introduced, new technologies are sprouting in the LED field like bamboo shoots after rain, and we are happy to see it. So, what kind of innovative trends does the LED display industry contain in this eye-catching first half of the year? In this article, Huicong LED Screen Network summarizes and sorts out the technological breakthroughs in the LED industry in the first half of the year for everyone to appreciate together.

The latest progress in the field of perovskite LEDs
In recent years, in addition to foreign teams advancing the research of perovskite LEDs, major domestic universities have also been conducting related research. First, let's take a look at the latest progress abroad - the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology has developed an excellent 100% pure perovskite blue LED.
According to Korean media reports, the research team of Professor Li Zhenglong of the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering at KAIST announced on July 10 that they have developed a revolutionary technology that fundamentally solves the color shift and low illumination problems of deep blue perovskite LEDs under driving voltage changes.
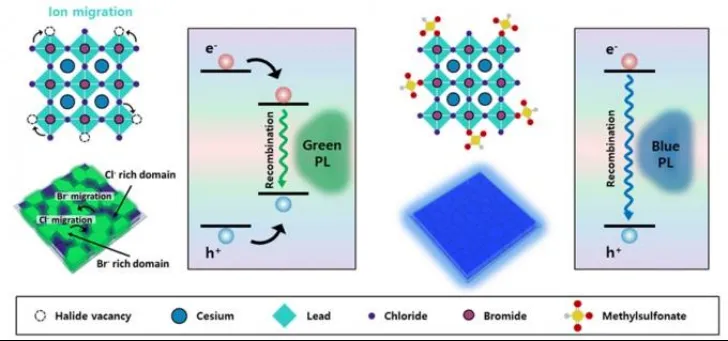
The team proposed an innovative solution to the long-standing problem of deep blue region in high color purity perovskite LEDs. Specifically, traditionally, perovskite LEDs composed of a mixture of multiple halogen ions tend to experience color fluctuations under different driving conditions. This is because halide vacancies act as halogen ion transmission channels, triggering a chain migration effect of surrounding ions. In response to this, the research team proposed a "chloride ion vacancy targeted ligand strategy". The targeted ligand strategy for chloride ion vacancies is that among the positive ion vacancies that are considered to be crystal structure defects, only chloride ion vacancies are specific and effectively eliminate these vacancies.
The research team said that the study effectively solved the problem of long-term color instability of mixed halogen ion perovskite deep blue LEDs, enabling perovskite deep blue LEDs to achieve a brightness of more than 2000 nits, narrowing the gap with green and red LEDs. In the future, perovskite deep blue LEDs can be used in LED displays.
Perovskite LED external quantum efficiency exceeds 30%
The team of Academician Huang Wei of Northwestern Polytechnical University, Associate Professor Zhu Lin of Nanjing University of Technology, and Professor Wang Jianpu of Changzhou University have made a major breakthrough in the field of perovskite light-emitting diode (LED) research: by accelerating the radiation recombination rate, significantly improving the fluorescence quantum efficiency, making perovskite The external quantum efficiency of mineral LED has exceeded the 30% mark, approaching the industrialization level.

The team creatively proposed a method to control crystal growth to generate a perovskite crystal phase with a faster radiative recombination rate, thereby significantly improving the fluorescence quantum efficiency. At the same time, the team successfully maintained the sub-micron structure of the three-dimensional perovskite, so that the light extraction efficiency of the device was not affected, achieving a two-pronged effect. As a result, this research achieved a fluorescence quantum efficiency of 96% and a light extraction efficiency of greater than 30%, and further prepared a high-efficiency perovskite LED with an external quantum efficiency of 32%, once again setting a world record for perovskite LED luminous efficiency. .
Achieving Stable Red Perovskite Quantum Dot LEDs
It is reported that Professor Wang Ning’s team and collaborators once again published a research paper titled “Fabrication of red-emitting perovskite LEDs by stabilizing their octahedral structure” in the Nature journal.
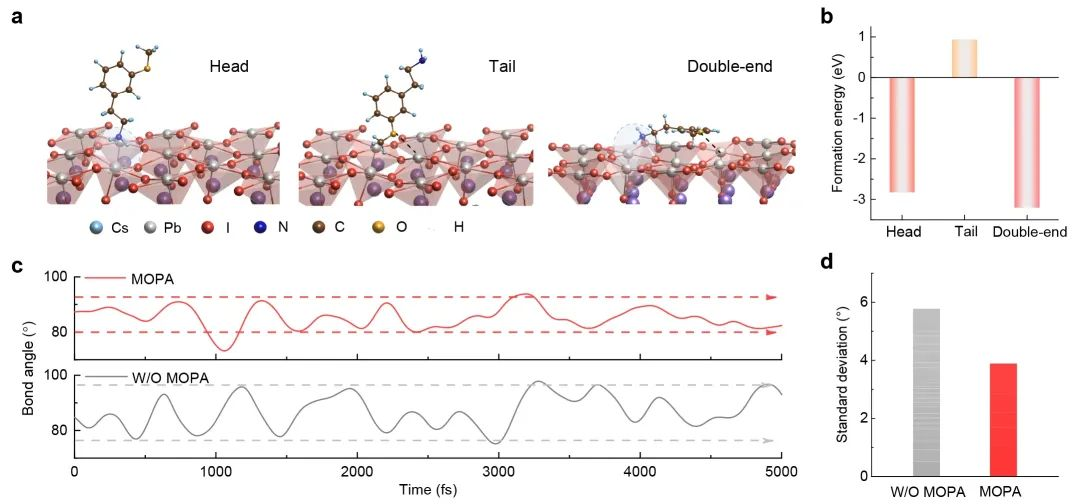
This research work revealed for the first time a new mechanism to fundamentally stabilize the octahedral structural unit of pure iodine-based perovskite, and demonstrated its application in efficient and stable pure red PeLEDs; it effectively solved the scientific problem that pure iodine-based perovskite is difficult to achieve efficient electroluminescence in the pure red light band, and provided a powerful link for the perovskite display technology based on the three primary colors, which is expected to provide key technical support for the future new high-definition display and information technology.
Latest progress in the field of Micro LED
Seoul University team develops flexible Micro LED connection technology
According to foreign media reports, a research team led by Yongtaek Hong, a professor in the Department of Electrical and Information Engineering at Seoul National University, announced that the team has developed a new technology that can connect Micro LEDs to flexible and stretchable devices. It is reported that the researchers used dip coating technology to selectively pattern the adhesive precursor onto the surface of the microdevice. The adhesive contains ferromagnetic particles that can be self-assembled into anisotropic chains using a magnetic field. This method can provide low contact resistance for device interconnection, and there is no electrical interference between fine-pitch terminals.
In addition to being able to assemble flexible and stretchable Micro LED arrays, this technology can also be used to create a Micro LED display device that can be attached to the skin, detect human body temperature and visualize the data on the display. The research team stated that this new technology can systematically integrate high-performance microelectronic devices while maximizing the mechanical properties of flexible and stretchable systems. The technology will contribute to the commercialization of flexible displays.
Domestic researchers develop Micro LED high-efficiency backlight devices
Foreign media reported that researchers from many universities in China have jointly developed an innovative self-polarizing RGB display device based on semi-polar Micro LED and perovskite film materials, which can significantly improve the performance of backlight technology. This research was completed by a team led by Professor Wu Tingzhu. They designed a unique device architecture that contains blue semipolar Micro LEDs that emit inherently polarized light. These Micro LEDs not only emit light by themselves, but can also be used as an excitation light source, combined with a perovskite color conversion layer with an anisotropic structure, to realize an RGB full-color polarized light-emitting device.

This achievement not only marks an important progress in the field of display technology, but also provides a new design direction for future display devices, indicating that more efficient and colorful display technology will soon enter the market.
Lighting up 403PPI full-color Micro LED display module
It is understood that the Xiamen Future Display Technology Research Institute of the Jiageng Innovation Laboratory successfully lit up a 1.63-inch Micro-LED full-color display module for smart wearables and mobile terminals, with a resolution of 403 pixels per inch, which is the highest resolution product currently achieved by my country using mass transfer technology. This achievement has been completed at Tianma Microelectronics Company and will be promoted and applied in the local display industry. The technical achievement was reported by CCTV News Network as "a new breakthrough in the field of new displays currently using mass transfer technology in my country."

According to the data, Jiageng Innovation Laboratory Xiamen Future Display Technology Research Institute has built the world's leading 2.5-generation Micro-LED process demonstration line and collaborated with upstream and downstream enterprises in the industry chain to tackle key problems, including epitaxial structure design, chip process manufacturing, transfer integration, etc. Advanced artificial intelligence methods are widely introduced in the technology development process, which greatly shortens the research and development cycle, saves development costs, and improves yield and efficiency. Focusing on the key mass transfer technology in the process development of TFT-based Micro-LED display panels, the research and development team of the institute took less than half a year to open up the process of high-efficiency, high-precision selective laser transfer, bonding, detection and repair. With the entire process, the transfer efficiency reaches 36 million pieces/hour (10,000 pieces/second), and a transfer yield of 99.999% has been achieved.
Core/shell colloidal quantum well technology significantly improves the efficiency of LED devices
It is understood that the team of Professor Liu Chuan and Associate Professor Liu Baiquan from the School of Electronics and Information Engineering (School of Microelectronics) of Sun Yat-sen University has made important progress in the field of light-emitting diodes (LEDs). They used core/shell colloidal quantum well technology to precisely control exciton dynamics, effectively reducing exciton recombination defects, balancing charge injection, and suppressing energy transfer between colloidal quantum wells. This innovative method not only significantly improves the efficiency of LED devices, but also successfully integrates them with thin film transistors and circuit boards to achieve active addressing, a display with a "pipeline" effect.
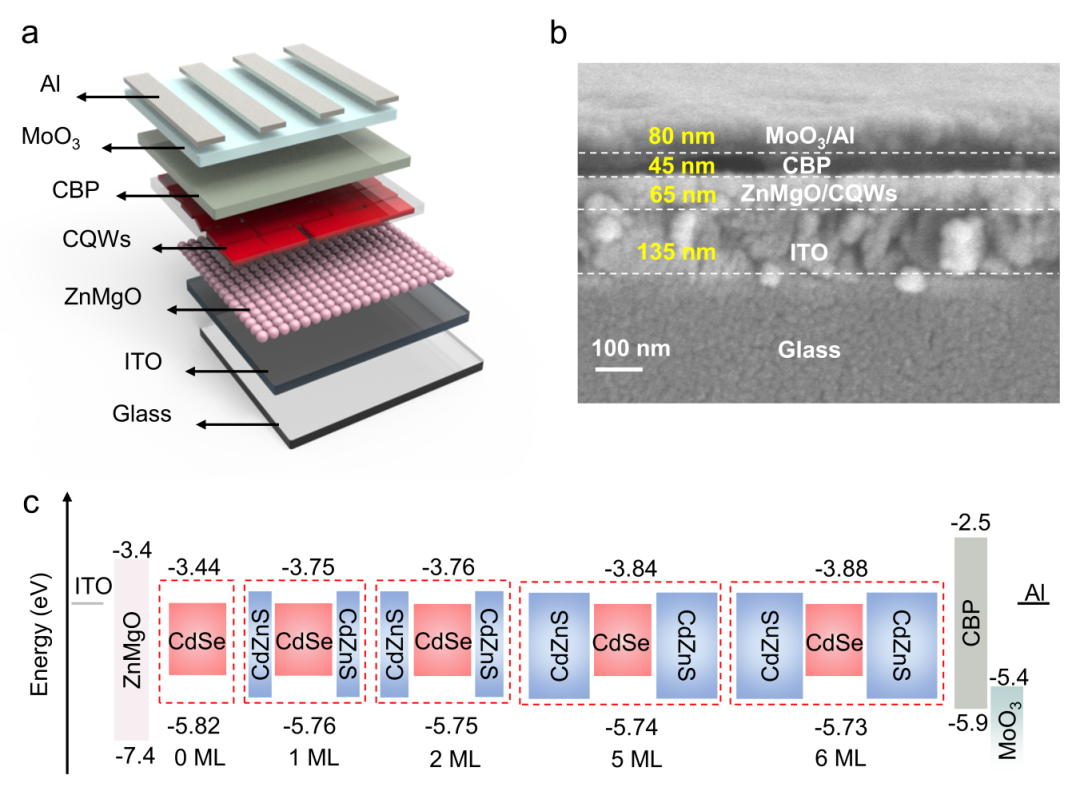
Colloidal quantum well LED, as a new type of nanocrystalline LED, has application potential in the display field due to its advantages such as high color purity, narrow half-width electroluminescence performance and solution processing. By deeply exploring the impact of core/shell heterogeneous colloidal quantum wells with different shell thicknesses on exciton dynamics, the team revealed the strong dependence between exciton production and the shell thickness of the colloidal quantum well. Research has found that increasing the shell thickness within a certain thickness range can significantly improve the radiative recombination efficiency and reduce Auger recombination, thus greatly improving the overall performance of colloidal quantum well LED devices. This achievement not only opens up a new path for further research and application of colloidal quantum well LEDs, but also provides new ideas and strategies for the development of future display and lighting technologies.
"There is no end to innovation and there is no limit to the future." This sentence seems to confirm the true meaning of the endless growth of the LED market. But it is worth noting that this also puts forward higher requirements for each player. How to focus on the direction of product iteration and take a differentiated path to break through and win? It is still a must-answer question for every enterprise. It is worth noting that many new policies in the first half of 2024 also involve the LED display industry. We have reason to believe that in the days to come, China's LED display industry will continue to make breakthroughs in research and development and implement industrialization with policy support, and continue to play an important role on the global technology stage.







 Hot News
Hot News